Topic: Economic Analysis & Policy
What the plastic surgery industry can tell us about the path of the economy
Revising the merger guidelines: Highlights from an expert panel discussion on the path forward in antitrust
To protect democracy, revive local journalism
To antitrust enforcers, consumers are irrelevant
Points of Pride
Moments showcasing Haas’ pioneering impact on the business world
From its outset, business at Berkeley has proved trailblazing. Launched by a gift from Cora Jane Flood in 1898, Berkeley Haas—previously called the College of Commerce and the School of Business—is the only leading business school founded by a woman, the first founded at a public university, and the second-oldest in the U.S. It was launched, in part, to help California expand economically, with the forward-looking goal of enriching trade and cultural exchange in the Pacific Rim. Throughout the twentieth century, business schools—and Berkeley Haas in particular—took on evermore prominent roles in shaping the world economy and the character of business itself. In this, our 125th year, we celebrate some of Haas’ pivotal moments reimagining business and business education.
Pioneering the study of social impact…

Professor Earl Cheit ushered in the study of corporate social responsibility via his research and teaching starting in the late 1950s. The future dean also organized the first national CSR symposium in 1964. New coursework, with support from Professors Dow Votaw and Edwin Epstein, became the model for leading business schools. Today, Haas prepares students to become ethical, socially focused leaders via myriad courses, experiential learning opportunities, and co-curricular activities.
…helped pandemic-ravaged small businesses.
Professors Adair Morse and Laura Tyson worked with the State of California and the nonprofit and banking sectors to create a public-private partnership as a small business loan fund for vulnerable companies. They then launched the California Rebuilding Fund for small businesses in under-resourced communities.
…created a competitive advantage.
The Center for Responsible Business, founded by faculty member Kellie McElhaney in 2002, brought Haas to the forefront of the corporate social responsibility and business sustainability movements. The Wall Street Journal ranked Haas the No. 2 b-school for CSR in 2006 and 2007. The Financial Times rated Haas No. 1 worldwide in 2008.
…launched the first and largest student-led SRI fund.
Debuting in 2008 and featured in the Wall Street Journal, the Socially Responsible Investment Fund (now called the Sustainable Investment Fund) offers MBA students real-world experience in delivering strong financial returns and positive social impact. Student fund managers have grown the $1 million investment to over $4 million.
…prioritized socially conscious entrepreneurship worldwide.
The Global Social Venture Competition, launched in 1999 by five Haas MBA students, turned the nascent idea of creating viable companies with social impact into a global triumph. In its 20 years of existence, the GSVC distributed more than $1 million in prize money and helped more than 7,000 teams better the world.
 Codifying our culture…
Codifying our culture…
Our Defining Leadership Principles Question the Status Quo, Confidence Without Attitude, Students Always, and Beyond Yourself had been latently capturing Haas’ essence for generations. In 2010, spearheaded by then-Dean Rich Lyons, BS 82, and anchored by the organizational culture research of Professor Jennifer Chatman, we took them public.
…distinguishes us from other prestigious business schools.
Our DLPs are a source of competitive advantage as well as pride and engagement. They are also our leadership brand, defining our graduates as Berkeley Leaders who practice responsible business. In 2018, Poets&Quants deemed us “the archetype for a values-driven MBA program.”
…positions Haas as the powerhouse for culture research.
Our new Berkeley Culture Center, founded and led by Professors Chatman, PhD 88, and Sameer Srivastava, helps business leaders create and nurture healthy and effective workplace cultures and is a hub for connections between academic research and corporate best practices. An annual conference convenes leaders from industry and academia to discuss new research and explore how to help organizations function more effectively. Chatman and Srivastava will soon launch the Culture Fix podcast to offer solutions to work dilemmas.
…cultivates community.
Since 1994, the alumni relations program at Haas has flourished in its mission to connect alumni to the school and to one another by adding traditions and signature events, expanding regional chapters and affinity/identity groups, developing career resources, creating a volunteer pipeline, providing mentorship opportunities for students and alumni, and much more.
Catalyzing the study of innovation…
The groundbreaking theories of dynamic capabilities, created by Professor David Teece in 1997, and open innovation, created by Adjunct Professor Henry Chesbrough, PhD 97, in 2003, led Haas to become one of the top business schools for innovation management and strategy.
…changed business education.
Previously, common belief held that established corporate structures were poorly suited for innovation, but Teece’s dynamic capabilities framework explains how large organizations can be entrepreneurial too. He also launched interdisciplinary programs with Berkeley’s engineering and law schools to help infuse innovation deep into research and teaching at Haas and to apply innovation management principles in private and public settings, including in the management of universities.
…facilitates global companies sharing innovative solutions.
Haas’ Garwood Center for Corporate Innovation helps companies expand markets, manage innovation, and facilitate strategic alliances via the membership-based Berkeley Innovation Forum. The World Open Innovation Conference, founded by Chesbrough and now hosted by a university in the Netherlands, allowed Haas to play a key role in bringing novel ideas to market.

…commercializes cleantech advancements.
The Cleantech to Market accelerator program pairs students with entrepreneurs to help bring promising climate tech innovations to market—more than 120 since its launch 15 years ago.
…helps students make innovation a competitive advantage.
The semester-long Haas@Work course acts as a faculty-run/student-staffed innovation agency—with teams of MBAs using a variety of innovation methodologies to assist corporate partners in developing and testing novel solutions to key challenges.
…inspires changemakers.
The Berkeley Changemaker initiative, established in 2020 and inspired by Lecturer Alex Budak’s Becoming a Changemaker course (later a book), has helped thousands of incoming students identify their passions and use their leadership traits to transform Berkeley and the world. Offered through the College of Letters and Science and Haas, the class is part of the campuswide initiative led by Laura Hassner, EMBA 18, and supported by former Dean Rich Lyons, BS 82, Berkeley’s chief innovation and entrepreneurship officer.
Early teaching of entrepreneurship…

Begun in 1970 (six years before Apple Computer was founded), Dean Richard Holton initiated one of the nation’s first courses in entrepreneurship, which he team-taught with Leo Helzel, MBA 68, for many years. It was likely the only such class that provided students direct contact with entrepreneurs. When the Lester Center for Entrepreneurship & Innovation opened in 1991, Executive Director Jerome Engel continued building Haas’ renowned entrepreneurship curriculum by partnering with the venture capital community, creating career opportunities for students, and training faculty worldwide.
…allowed Haas to pioneer the Lean LaunchPad method.
Created in 2011 by Lecturer Steve Blank and now taught worldwide, Lean LaunchPad was an entirely new way to teach entrepreneurship. Inspired by a Haas MBA course, it challenges students to develop business models rather than business plans and to iterate their models frequently based on customer feedback.
…inspires unlikely entrepreneurs.
Professor Toby Stuart changed entrepreneurship teaching at Haas by restructuring the full-time MBA entrepreneurship course, gearing it not only to students with startup ideas but to students investigating entrepreneurship as a career as well. He also created a star-studded, career-changing Silicon Valley Immersion Week for the Berkeley MBA for Executives Program.
…positions Haas as the campus entrepreneurship hub.
A new entrepreneurship and innovation initiative, spearheaded by Dean Ann Harrison, is enhancing Haas’ efforts on three fronts: endowing thought leadership through faculty chairs, expanding programming, and creating a three-floor Entrepreneurship Hub for all of campus. Renovation has begun on the Hub, which is adjacent to Haas and features spaces for students to gather and work.
Dominating in finance…
In the late 1960s, when students were requesting courses providing creative approaches to financial markets and investment theory (thanks to new technologies), Berkeley embraced an innovative and highly quantitative approach to finance, becoming a national leader with its analytical quantitative curriculum.
 …prompted insights into financial markets.
…prompted insights into financial markets.
In the 1970s, Professor Emeritus Mark Garman pioneered early stock exchange simulations and studied market microstructures, minute trading activity in asset markets that today play a role in algorithmic and electronic trading.
…changed how financial assets are created and priced.
In 1979, the late Professor Emeritus Mark Rubinstein developed the binomial options pricing model (aka the Cox-Ross-Rubinstein model), which can be used to price a range of complex options. It remains one of Wall Street’s most important valuation tools and no doubt contributed to the subsequent growth of derivatives. In the early 1990s, Rubinstein, Professor Hayne Leland, and Adjunct Professor John O’Brien launched the SuperTrust, an S&P 500-based fund that traded as a single security, essentially the first exchange-traded fund.
…allowed us to take the lead in the crowdfunding revolution.
In 2008, Danae Ringelmann and Eric Schell, both MBA 08, co-founded Indiegogo, one of the world’s first crowdfunding sites, democratizing access to capital and entrepreneurship while navigating unchartered regulatory waters. In 2015, Haas, the Fung Institute for Engineering Leadership, and the Kauffman Foundation partnered to establish CrowdBerkeley, a premier hub of education and research on crowdfunding.
Championing new teaching modalities…
As business evolved, Haas adapted its teaching to respond to challenges and opportunities taking shape worldwide, often blazing new academic trails. In 1959, when the famous Ford Foundation and Carnegie Corporation reports criticized most of American business education for its overall low standards and overly strong vocational bent, both cited Berkeley’s program, which was broader and more rigorous, as an excellent model.
…led to the first MFE Program at a business school.
The Master of Financial Engineering Program was launched in 2001 to prepare students to use skills in math, theoretical finance, and computer programming to make technically complex financial decisions. Today, it consistently ranks first among programs nationwide. The program recently added a data science curriculum that’s supported by a high-tech lab offering students and faculty access to real-time financial data and leading analytical software.
…created one of the few international management consulting programs.
Our International Business Development course debuted in 1992, assigning teams of MBA students to real-world consulting projects that include several weeks overseas, mostly in developing economies. IBD has since dispatched more than 1,800 students to work in 89 countries, helping organizations worldwide redefine how they do business.

…made Haas the first Top 10 b-school to offer a remote MBA.
In 2021, Haas announced its Flex cohort for the evening & weekend program. Students take live, virtual core courses from Haas professors teaching in new state-of-the-art video classrooms and can choose to take their electives virtually or on campus. (See sidebar, Linking Up.)
…offers unprecedented education of cross-sector leaders.
The Center for Social Sector Leadership, founded by Nora Silver, who serves as faculty director, pioneered three unique experiential b-school programs to prepare students for the nonprofit and public sectors. Social Sector Solutions, a professional management consulting partnership between Haas and McKinsey, launched in 2006 and has involved over 900 students who have served 170 nonprofits and public/social enterprises. Philanthropy Fellows, begun in 2008, is a partnership with the David and Lucile Packard Foundation that places recent MBAs with program officers at the foundation for two years—allowing new grads to enter a foundation at a professional (rather than administrative) level. Impact CFO, created with Assistant Professor Omri Even-Tov, will launch this fall with 15–20 alumni to help meet the market demand for chief financial officers in social impact organizations.
…integrated problem framing and solving approaches into a business curriculum.
Teaching Professor Sara Beckman developed three pioneering b-school courses: Managing the New Product Development Process and Design as a Strategic Business Issue (both in 1993), and Problem Finding, Problem Solving, which was part of the MBA core starting in 2012. PFPS, which included everything from systems thinking to human-centered design approaches, taught students how to think about complex business problems. Since 2017, undergrads can pursue the Berkeley Certificate in Design Innovation, a first-ever collaboration among Haas, the College of Engineering, the College of Environmental Design, and the College of Letters and Science’s Arts & Humanities Division.

Embracing behavioral economics…
Behavioral economics was born at UC Berkeley in 1987 with an interdisciplinary PhD course taught by two future Nobelists: economist George Akerlof and psychologist Daniel Kahneman. Professor Terrance Odean, MS 92, PhD 97, was encouraged by Kahneman to be the first at Haas to research behavioral finance, an area that was fertile ground for psychological analysis in an era of asset bubbles and market crises.
…established the vanguard of a new generation of behavioral economics researchers.
Haas faculty have since propelled the discipline into the mainstream while taking it into the future. Associate Professor David Sraer has investigated investor behavior and speculative bubbles. The late Professor John Morgan, who founded Haas’ Experimental Social Science Laboratory (XLab) for conducting experiment-based research, focused some of his work on inattention to shipping costs in eBay auctions and on behavioral biases in voting. Professor Ulrike Malmendier, the only woman ever to have won the prestigious Fischer Black Prize, has researched how individual biases affect corporate decisions, stock prices, and markets in general. She and Professor Stefano DellaVigna will lead the new O’Donnell Center for Behavioral Economics, which launches this fall, and will continue to make Berkeley the epicenter of behavioral economics research and a beacon for the brightest intellectual talent in the field.

Committing to diversity, equity, inclusion, justice, and belonging…
Socioeconomic mobility is core to both the UC Berkeley and Haas missions. The 2018 DEI strategic plan—the first such action plan at a major business school—translated aspirations for inclusion into intentional and comprehensive action at all levels of Haas. As a result, Haas has made substantive changes over the past six years to increase diversity and representation, engender lifelong learning around equity and inclusion, and cultivate belonging. Haas was also the first leading b-school to publicly share its DEI demographic data.
…created a unique and robust DEIJB team.
Dean Ann Harrison quickly made DEIJB a priority when she began her tenure in 2019. She met with student leaders; significantly increased scholarship funding for the incoming class; diversified the demographics of the Haas School Board, faculty, and senior leadership teams; modified the core MBA curriculum to require a course on leadership communications in diverse work environments; and appointed one of the first chief diversity, equity, and inclusion officers at a leading business school. Today, CDEIO Élida Bautista oversees a team of four focusing on admissions, student experience, staff community and capacity-building, and, uniquely, faculty support (see sidebar, Teaching Aid).
…advances gender and diversity in policy and business.
Research by Professor Laura Kray, a leading expert on the social-psychological barriers influencing women’s career attainment, has debunked popular gender stereotypes. Kray’s work has shown that the popular perception that men outperfom women as negotiators is false and hurts pay equity efforts. The Center for Equity, Gender & Leadership, founded in 2017 by faculty member Kellie McElhaney, develops “equity fluent” leaders to drive positive change and build an inclusive and equitable world. EGAL does this via hands-on education and learning opportunities, resources (like playbooks), and support for academic research. Kray is EGAL’s faculty director.
…improves access to Haas.
During the pandemic, Haas launched two programs to expand, diversify, and strengthen access to the school. Accelerated Access allows students who wish to pre-commit to business school while acquiring important work experience to apply to Haas in their senior year of college and gain conditional acceptance. Cal Advantage offers talented University of California undergraduates a streamlined application process.
…enriches the diversity of the venture community.
The Black Venture Institute, created by Berkeley Executive Education in collaboration with BLCK VC and Salesforce Ventures, teaches Black executives the foundational elements to become angel, scout, and venture investors.
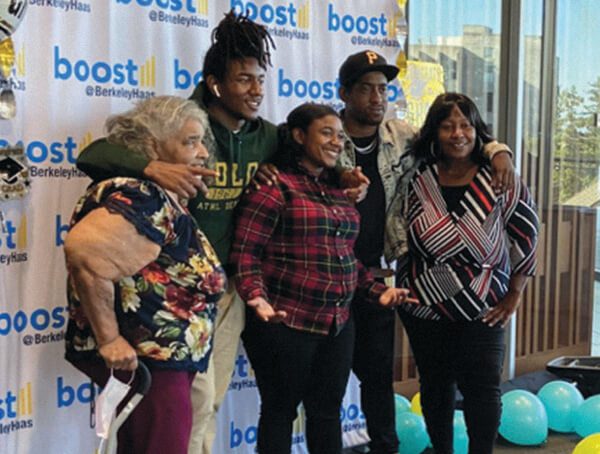
…provides social mobility opportunities for local youths.
In 1989, Dean Raymond Miles started the Boost@BerkeleyHaas program—formerly known as the East Bay Outreach Program then Young Entrepreneurs at Haas (YEAH)—to teach business and academic skills to under-resourced high school students. It is one of the only university-based youth entrepreneur programs to support teens from disadvantaged communities throughout their entire high school career. Since its founding, the program has helped more than 1,200 students (many first-generation) go to college.
…supports alumni professional development.
Alumni may enroll in a three-part, self-paced online DEI workshop featuring CDEIO Bautista that focuses on best practices for creating and promoting a diverse and inclusive workplace culture. Since 2021, alumni committed to DEIJB have gleaned insights from top industry leaders at the annual virtual Alumni Diversity Symposium.
…expands partnerships with HBCUs.
Haas recently launched an HBCU MBA Fellowship with founding gifts from five alumni. The first-of-its-kind endowment will provide tuition support to MBA students who have attended a Historically Black College or University.

Pioneering the study of urban economics…
The Center for Real Estate and Urban Economics was founded in 1950, one of the first such university centers nationwide. It allowed Professors Sherman Maisel and Albert Schaaf to author the first major study of the structure of the California real estate industry, looking at the role of race and gender and finding a rising trend of women employed in the field. Later, Maisel would help create the current national U.S. mortgage market that relies on bond financing rather than on the strength and liquidity of local banks.
…advanced an unprecedented analysis of real estate markets and risk management.
Professor Nancy Wallace and researchers at the Fisher Center for Real Estate and Urban Economics mapped the massive mortgage market and built groundbreakingly accurate housing price indices that monitor the characteristic dynamics of the housing stock. Wallace and Professor Richard Stanton, along with Paulo Issler, MBA 98, PhD 13, and Carles Vergara-Alert, MFE 04, PhD 08, recently combined these comprehensive databases with wildfire prediction models to estimate residential real estate value-at-risk in California.
…led to a renowned gathering of experts and a legendary forecast.
The Fisher Center hosts an annual Real Estate and Economics Symposium, a high-powered event known for the reputation of the speakers—and for Professor Emeritus Ken Rosen’s revered economic and real estate forecasts for California.
 Our commitment to sustainability…
Our commitment to sustainability…
No other business school matches the breadth of Haas’ work in sustainability. The new Office of Sustainability and Climate Change, led by climate finance expert Michele de Nevers, coordinates curriculum and activities in five key areas: energy, food and agriculture, the built environment, sustainable and impact finance, and corporate responsibility.
…launched the preeminent university research center on energy economics.
Ever since Professor Severin Borenstein began leading the Energy Institute at Haas in 1994, it has been a place where serious academic researchers influence public policy at the state and federal levels, where the curriculum in energy and cleantech evolves to meet student and marketplace needs, and where collaboration flourishes. No other business school has as much depth, breadth, or influence in the energy field as Haas. Borenstein also co-developed the unique—and indispensable—Energy and Environmental Markets course and the energy market simulations used in the class. The course was the first of its kind at a top b-school and has been emulated at many peer institutions.
…allows Haas to pioneer green architecture and operations.
Chou Hall, which opened in 2017, is the nation’s greenest academic building, having earned LEED Platinum certification for its energy efficient design and operation, TRUE Zero Waste certification at the highest level after more than a year of efforts to divert over 90% of landfill waste, and WELL Gold, which is given to buildings that promote user health and well-being. Haas recently appointed its first full-time director of campus sustainability to oversee numerous initiatives—such as the campus renewable energy transition and elimination of single use plastic—to move Haas to carbon neutrality by 2025.
…inspired an unrivaled array of sustainability courses.
In 2021, Professor Nancy Wallace shifted the focus of the real estate program to consider high-efficiency, mixed-use development and financing strategies to fund real estate sustainability. Haas faculty members are now retooling all core MBA courses to address climate change and other sustainability challenges in various business disciplines. The revamped Sustainable and Impact Finance program keeps pace with rapid changes in climate finance and impact investing to best prepare students for careers. One focus for the Center for Responsible Business is reimagining capitalism and Executive Director Robert Strand, who teaches a course called Sustainable Capitalism in the Nordics?, is now the executive director of the new UC Berkeley Nordic Center.
…led to new degrees and certificates.
With Berkeley’s Rausser College of Natural Resources, Haas offers an undergraduate minor in sustainability and is developing a dual MBA/master’s in climate solutions. Haas also offers the Michaels Graduate Certificate in Sustainable Business.
Our faculty’s public service work…
Since its earliest days, Haas faculty have applied their insights to issues advancing the public good. Our first dean, Carl Copping Plehn, is credited as one of the fathers of the California tax system. Professor Lincoln Hutchinson, an expert in South America and Russia, left Berkeley in 1922 to become one of the State Department’s earliest commercial attachés. In the 1930s, Dean E.T. Grether lent his expertise of markets and pricing structures to the Great Depression’s wave of business regulations—among many others.

…guides national economic policy in groundbreaking ways.
Professor Emeritus Janet Yellen is the first person to have served in the nation’s three top economic roles: treasury secretary, head of the Federal Reserve, and chair of the President’s Council of Economic Advisers (during the Clinton administration). Her four years as Fed chair were considered near perfect, marked by job and wage growth amid low interest rates. Former dean Laura Tyson was the first woman to chair the Council of Economic Advisers (1993–95) and to direct the National Economic Council (1995–96), among other roles.
…helped navigate e-commerce, communications, and horizontal mergers.
As the chief economist for the Federal Communications Commission in the mid-1990’s, Professor Emeritus Michael Katz informed an important revision of cable television price regulations. He later addressed Congress about how to allow consumers to safely make payments via phones. Professor Emeritus Carl Shapiro played a central role in the first big update in almost 20 years of the guidelines on horizontal mergers as the chief economist in the Antitrust Division of the U.S. Department of Justice (2009–11). Both men continue to serve as expert witnesses in the country’s most high-profile antitrust cases.
…advances global gender parity.
As a longtime co-author of the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report, Tyson helped quantify the magnitude of gender-based disparities and develop initiatives for change. She also served as lead author in 2016 for two reports for the UN Secretary-General’s High-Level Panel on Women’s Economic Empowerment that included action-oriented recommendations to hasten improved economic outcomes for women.
…gives voice to the voiceless.
A former World Bank director, Dean Ann Harrison has earned international acclaim for her research on foreign direct investment and multinational firms. In proving that job losses in U.S. manufacturing are driven primarily by labor-saving technology such as investments by U.S. multinationals in automation, she has shown that free-trade economists miscalculated the costs of globalization and failed to ensure that policies were in place to compensate the losers, including many workers in rural communities.